RancherOS
I first heard about Rancher back in November 2015. I figured I would give RancherOS another look and see how it’s doing.
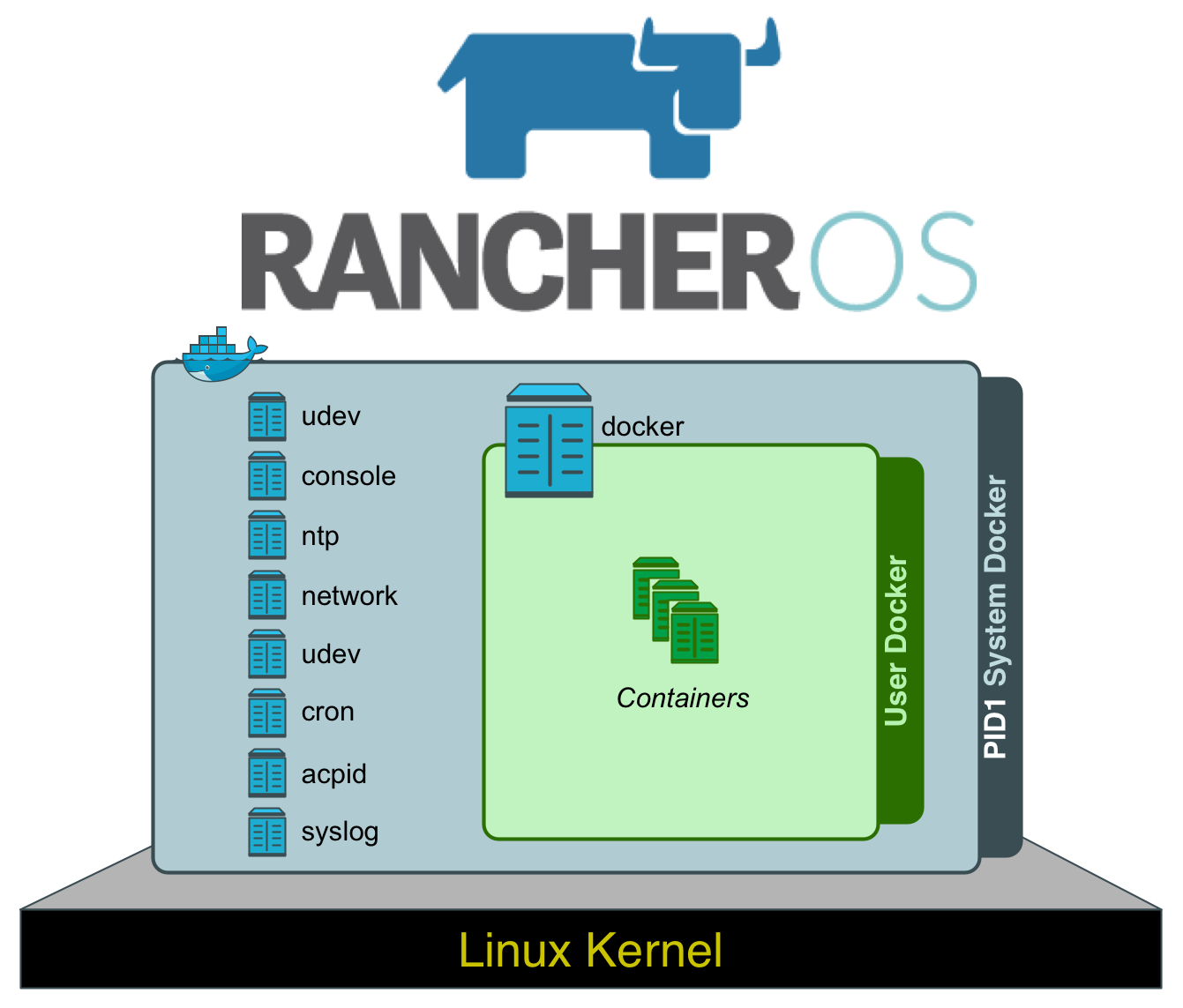
RancherOS has an intreguing concept: A base OS that uses Docker containers for everything in the userspace.
RancherOS
- Rancher OS : A Tiny Linux Distribution designed for running Docker Containers.
- A novel feature of RancherOS is that it operates all userspace functionality as a Docker container.
- Download iso from https://github.com/rancher/os/releases
wget -o rancher-1.4.1.iso \
https://github.com/rancher/os/releases/download/v1.4.1/rancheros.iso- RancherOS has two Docker Daemons: a system-level and a user-level.
- The system-docker command is used for accessing and controlling the system-level Docker daemon.
- The docker command is used for accessing and controlling the user-level Docker daemon.
-
After booting, the system-docker ps command will list all of the system-level Docker containers.
- Rancher does not have an init system.
- Any commands to be run on startup must be placed in /opt/rancher/bin/start.sh
Run cAdvisor Docker on the System level
system-docker pull google/cadvisor:latest
system-docker run -d \
-p 8080:8080 \
-v /:/rootfs:ro \
-v /var/run:/var/run:rw \
-v /sys:/sys:ro \
-v /var/lib/docker/:/var/lib/docker:ro \
--net=host --name cadvisor google/cadvisor:latestInstall to Disk
- Boot from the ISO
- Use the ros install command to install to a disk.
cat << EOF > mycloudconfig.yaml
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDV+7gd7uDd0kxynaFSCjus0NOECHfmADvS1GswNKGYhg4Dd2YMAYPi9OvUgBonrIUYHV8t6mcc6KdpVmuzGGSOfbPgbh+LmQT/7rdCgXDXGNuMBV6J8hDEyV6SPFoMsILAiUX2BPegmfC8F4bdUB4bIoHwm2bR6nEUs1qjPVSqjznS0s4MWzXtcUc7pciDMXYtaJ+NI/LvFfZD/XIrpVaG+JuW8TSDb4pqyMUS9Lkp2UAYKOphwmyZ5vliTv9sGvWyzfAXDe0cTlr1mV71V7YVUc8AMY8GRgaVqGvd4avNLzTmUMkultumFcdQCxZ6gSxBI8QV+kSb+4cWD8oDFbWR devon@Devons-MacBook-Air
EOF
fdisk -l /dev/sda
echo -e "o\nw\n" | fdisk /dev/sda
fdisk -l /dev/sda
ros install -c mycloudconfig.yaml -d /dev/sda- The cloud-config file will be written to /var/lib/rancher/conf/cloud-config.yml and can be modified any time.
- After installation, the system will not boot to an interactive console.
Cloud-Config
- RancherOS state is controlled by a cloud-config file.
- On AWS, RancherOS supports loading the cloud-config from the user-data.
- On-Disk, RancherOS stores the cloud-config data in /var/lib/rancher/conf/cloud-config.yml
#cloud-config
rancher:
console: ubuntu
ssh_authorized_keys:
- ssh-rsa AAA...ZZZ example1@rancher
- ssh-rsa BBB...ZZZ example2@rancherros command
- The ros command is used to edit the configuration of the system
- To see the DNS configuration of the system: ros config get rancher.network.dns.nameservers
- Export the current cloud-config: ros config export
- Validate a cloud-config file: ros config validate -i cloud-config.yml
RancherOS Console
- The RancherOS console is itself a Docker container.
- The RancherOS console uses BusyBox by default.
- The RancherOS console can be switched to another docker-based OS, like Ubuntu.
- To switch the RancherOS console, use the ros command: ros console switch ubuntu
- RancherOS Supported Consoles are:
- default (busybox)
- alpine
- centos
- debian
- fedora
- ubuntu
ros console list
ros console switch ubuntu- The non-default consoles share /home and /opt with the underlying host, so any changes made there will not be lost between reboots.